Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yabuuchi, Kiyohiro*; Suzudo, Tomoaki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 574, p.154161_1 - 154161_6, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In nuclear materials, irradiation defects cause degradation of mechanical properties. In these materials, the relationship between dislocations and voids is particularly important for mechanical strength. Although only spherical voids have been studied in the past, this study focuses on faceted voids, which are observed simultaneously with spherical voids. In the current study, molecular dynamics was used to analyze the effect of faceted voids in the irradiation hardening of pure iron. Specifically, we clarified the difference in obstacle strength and interaction processes between spherical voids and faceted voids, and that even faceted voids show differences in interaction depending on their crystallographic arrangement with dislocations.
Yano, Yasuhide; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Tanno, Takashi; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 9 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)The effects of fast neutron irradiation on tensile properties of modified 316 stainless steel (PNC316) claddings and wrappers for fast reactors were investigated. PNC316 claddings and wrappers were irradiated in the experimental fast reactor Joyo at irradiation temperatures between 400 and 735  C to fast neutron doses ranging from 21 to 125 dpa. The post-irradiation tensile tests were carried out at room and irradiation temperatures. Elongations of PNC316 measured by the tensile tests were maintained at an engineering level, although the material incurred significant irradiation hardening and softening. The maximum swelling of PNC316 wrappers was about 2.5 vol.% at irradiation temperature between 400 and 500
C to fast neutron doses ranging from 21 to 125 dpa. The post-irradiation tensile tests were carried out at room and irradiation temperatures. Elongations of PNC316 measured by the tensile tests were maintained at an engineering level, although the material incurred significant irradiation hardening and softening. The maximum swelling of PNC316 wrappers was about 2.5 vol.% at irradiation temperature between 400 and 500 C up to 110 dpa. Japanese 20% cold-worked austenitic steels, PNC316 and 15Cr-20Ni, had sufficient ductility and work-hardenability even after above 10 vol.% swelling, while they had very weak plastic instabilities.
C up to 110 dpa. Japanese 20% cold-worked austenitic steels, PNC316 and 15Cr-20Ni, had sufficient ductility and work-hardenability even after above 10 vol.% swelling, while they had very weak plastic instabilities.
 C in JMTR
C in JMTRWakai, Eiichi; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Tomita, Hideki*; Furuya, Kazuyuki; Sato, Michitaka*; Oka, Keiichiro*; Tanaka, Teruyuki*; Takada, Fumiki; Yamamoto, Toshio*; Kato, Yoshiaki; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 343(1-3), p.285 - 296, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:93.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The dependence of helium production on radiation-hardening and -embrittlement has been examined in a reduced-activation martensitic F82H steel doped with  B,
B,  B and
B and  B+
B+ B irradiated at 250
B irradiated at 250 C to 2.2 dpa. The total amounts of doping boron were about 60 massppm. The range of He concentration produced in the specimens was from about 5 to about 300 appm. Tensile and fracture toughness tests were performed after neutron irradiation. 50 MeV-He
C to 2.2 dpa. The total amounts of doping boron were about 60 massppm. The range of He concentration produced in the specimens was from about 5 to about 300 appm. Tensile and fracture toughness tests were performed after neutron irradiation. 50 MeV-He irradiation was also performed to implant about 85 appm He atoms at 120
irradiation was also performed to implant about 85 appm He atoms at 120 C by AVF cyclotron to 0.03 dpa, and small punch testing was performed to obtain DBTT. Radiation-hardening of the neutron-irradiated specimens increased slightly with increasing He production. The 100 MPam
C by AVF cyclotron to 0.03 dpa, and small punch testing was performed to obtain DBTT. Radiation-hardening of the neutron-irradiated specimens increased slightly with increasing He production. The 100 MPam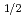 DBTT for the F82H+
DBTT for the F82H+ B, F82H+
B, F82H+ B+
B+ B, and F82H+
B, and F82H+ B were 40, 110, and 155
B were 40, 110, and 155 C, respectively. The shifts of DBTT due to He production were evaluated as about 70
C, respectively. The shifts of DBTT due to He production were evaluated as about 70 C by 150 appmHe and 115
C by 150 appmHe and 115 C by 300 appmHe. The DBTT shift in the small punch testing was evaluated as 50
C by 300 appmHe. The DBTT shift in the small punch testing was evaluated as 50 C.
C.
Ando, Masami; Wakai, Eiichi; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Matsukawa, Shingo; Naito, Akira*; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Oka, Keiichiro*; Tanaka, Teruyuki*; Onuki, Somei*
JAERI-Review 2004-025, TIARA Annual Report 2003, p.159 - 161, 2004/11
The objectives of this study are to evaluate radiation hardening on ion-irradiated F82H up to 100 dpa and to examine the extra component of radiation hardening due to implanted helium atoms (up to  3000 appmHe) in F82H under ratio of 0, 10, 100 appmHe/dpa.The ion-beam irradiation experiment was carried out at the TIARA facility of JAERI. Specimens were irradiated at 633 K by 10.5 MeV Fe ions with/without 1.05 MeV He ions. Micro-indentation tests were performed at loads to penetrate about 0.40 mm in the irradiated specimens using an UMIS-2000. The results are summarized as follows:1) As a result of the single irradiated F82H, the micro-hardness tended to increase about 30 dpa. 2) The extra radiation hardening was obviously caused by co-implanted helium atoms more than 1000 appm in F82H irradiated at 633 K. 3) In the dual-beam (100 appmHe/dpa) irradiated microstructure, nano-voids and fine defects were observed. It is suggested that the formation of nano-voids causes the extra radiation hardening by helium co-implantation.
3000 appmHe) in F82H under ratio of 0, 10, 100 appmHe/dpa.The ion-beam irradiation experiment was carried out at the TIARA facility of JAERI. Specimens were irradiated at 633 K by 10.5 MeV Fe ions with/without 1.05 MeV He ions. Micro-indentation tests were performed at loads to penetrate about 0.40 mm in the irradiated specimens using an UMIS-2000. The results are summarized as follows:1) As a result of the single irradiated F82H, the micro-hardness tended to increase about 30 dpa. 2) The extra radiation hardening was obviously caused by co-implanted helium atoms more than 1000 appm in F82H irradiated at 633 K. 3) In the dual-beam (100 appmHe/dpa) irradiated microstructure, nano-voids and fine defects were observed. It is suggested that the formation of nano-voids causes the extra radiation hardening by helium co-implantation.
Ando, Masami; Wakai, Eiichi; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Furuya, Kazuyuki; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Takeuchi, Hiroshi; Oka, Keiichiro*; Onuki, Somei*; Koyama, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(2), p.1137 - 1141, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:93.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)One of the most crucial issues on R&D of reduced activation ferritic/martensitic steels is the effect of helium on the degradation of fracture toughness. The synergistic effects of displacement damage and helium on F82H steel can be partially simulated by martensitic steels doped with  B or
B or  Ni in a mixed spectrum fission reactor. However, the control of helium production rate is difficult and the chemical effects of B or Ni doping on mechanical property are not small. Therefore, multi-ion irradiation method is the most convenient and accurate method to simulate various irradiation conditions. Moreover, the effects of helium on irradiation hardening behavior can be examined by combining ion-irradiation with ultra micro-indentation technique. The purpose of this study is to examine the extra component of radiation hardening due to implanted helium in F82H. The extra component of irradiation hardening due to helium was hardly detected in the dual-beam irradiation. Therefore, the effect on irradiation hardening below 630K of helium (
Ni in a mixed spectrum fission reactor. However, the control of helium production rate is difficult and the chemical effects of B or Ni doping on mechanical property are not small. Therefore, multi-ion irradiation method is the most convenient and accurate method to simulate various irradiation conditions. Moreover, the effects of helium on irradiation hardening behavior can be examined by combining ion-irradiation with ultra micro-indentation technique. The purpose of this study is to examine the extra component of radiation hardening due to implanted helium in F82H. The extra component of irradiation hardening due to helium was hardly detected in the dual-beam irradiation. Therefore, the effect on irradiation hardening below 630K of helium ( 500 appm) was very small.
500 appm) was very small.
Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*; Sakasegawa, Hideo*; Klueh, R. L.*; Sokolov, M. A.*; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Koyama, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(1), p.283 - 288, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:75.17(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Reduced-activation ferritic/martensitic steels (RAFs) were developed as candidate structural materials for fusion power plants. In a previous study, it was reported that ORNL9Cr-2WVTa and JLF-1 (Fe-9Cr-2W-V-Ta-N) steels showed smaller ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) shifts compared to IEA modified F82H (Fe-8Cr-2W-V-Ta) after neutron irradiation up to 5 dpa at 573K. This difference in DBTT shift could not be interpreted as an effect of irradiation hardening, and it is also hard to be convinced that this difference was simply due to a Cr concentration difference. To clarify the mechanisms of the difference in Charpy impact property between these steels, various microstructure analyses were performed.
Wakai, Eiichi; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Yamamoto, Toshio*; Kato, Yoshiaki; Takada, Fumiki
Materials Transactions, 45(8), p.2638 - 2640, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.41(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Ando, Masami; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Kato, Yudai*; Koyama, Akira*; Nakamura, Kazuyuki; Takeuchi, Hiroshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 307-311(Part1), p.260 - 265, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:90.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Wakai, Eiichi; Miwa, Yukio; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*; Robertson, J. P.*; Klueh, R. L.*; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Abiko, Kenji*; Furuno, Shigemi*; Jitsukawa, Shiro
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 307-311(Part.1), p.203 - 211, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:82.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kawanishi, Hiroshi*; Suzuki, Masahide
Effects of Radiation on Materials (ASTM STP 1366), p.492 - 515, 2000/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:65.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 C
CNishiyama, Yutaka; Fukaya, Kiyoshi; Suzuki, Masahide; Eto, Motokuni
JAERI-Research 97-039, 29 Pages, 1997/06
no abstracts in English
Hishinuma, Akimichi; Jitsukawa, Shiro
Annales de Physique, 22(SUPPL.3), p.163 - 170, 1997/06
no abstracts in English
Ara, Katsuyuki; ; ; Sakasai, Kaoru
Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Pressure Vessel Technology (ICPVT-8), 1, p.183 - 189, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Masahide;
JAERI-Research 94-038, 23 Pages, 1994/11
no abstracts in English
*;
Trans.Iron Steel Inst.Jpn., 23, p.450 - 452, 1983/00
no abstracts in English
; ; Shiraishi, K.
Trans.Jpn.Inst.Met., 20(12), p.697 - 705, 1979/00
no abstracts in English
Shiraishi, K.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 20(9), p.620 - 625, 1978/09
Times Cited Count:0no abstracts in English
Shiraishi, K.
Denshi Kenbikyo, 12(1), p.15 - 20, 1977/01
no abstracts in English
 C
CShiraishi, K.; ; Katano, Y.
JAERI-M 6214, 20 Pages, 1975/08
no abstracts in English
 C
CShiraishi, K.; ; Katano, Y.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 57(3), p.361 - 364, 1975/03
Times Cited Count:13no abstracts in English